Consulting phone:
135-3037-2041
(Mr.Wang)
Product introduction:
Farad capacitor principle Farad capacitor and supercapacitor are extremely large capacitors with a capacitance of thousands of farad. The capacitance depends on the distance between electrodes and the surface area of electrodes. In order to obtain such a large capacitance, it is necessary to reduce the distance between electrodes of supercapacitors as much as possible and increase the surface area of electrodes. Therefore, the double-layer principle and activated carbon porous electrode are adopted.
Product specification:
| project | characteristic |
| working temperature | -40℃+65℃@2.7V -40℃+85℃@2.3V |
| Storage temperature | -40℃+70℃ |
| capacity | 100~600F |
| tolerance | 0+30% |
| Rated voltage | 2.7V |
| Surge voltage | 2.85V |
| temperature characteristic | Capacity change from - 40 ℃ to 65 ℃: △ c ∠ 20% of initial measured value @ 25 ℃ internal resistance change: △ ESR ∠ 100% of nominal value |
| High temperature load life | Under working temperature and rated voltage, load 1500h capacity change: △ c ∠ 20% of initial measured value @ 25 ℃ internal resistance change: △ ESR ∠ 100% of nominal value |
| Normal temperature load life | Under 25 ℃ and rated voltage, load capacity change in 10 years: △ c ∠ 20% of initial measured value @ 25 ℃ internal resistance change: △ ESR ∠ 100% of nominal value |
| Normal temperature cycle life | At 25 ℃, after 500000 charge-discharge cycles (from rated voltage to 1/2 rated voltage), capacity change: △ c ∠ 20% of initial measured value @ 25 ℃ internal resistance change: △ ESR ∠ 100% of nominal value |
| Storage life | Put it under no load for two years at 25 ℃ to meet the requirements of high temperature load life |
| Steady state hyperthermia | At 40 ℃, 90% RH and rated voltage, the load is 240h, meeting the requirements of high temperature load life |
series | Rated voltage V | Capacity F | DC internal resistance m Ω | AC internal resistance m Ω | Leakage current uA72hrs | Weight g | D*L(mm) | Energy density (Wh/kg) | Power density (Wh/kg) |
YKY | 2.7 | 100 | 12 | 8 | 0.3 | 20 | 22*45 | 5.1 | 7.6 |
2.7 | 200 | 10 | 6 | 0.7 | 36 | 30*50 | 5.6 | 5.1 | |
| 2.7 | 360 | 3.6 | 4 | 1.1 | 65 | 35*60 | 5.7 | 8.0 | |
2.7 | 400 | 3.2 | 2.8 | 1.0 | 70 | 35*60 | 5.8 | 8.1 | |
2.7 | 470 | 3.5 | 3 | 1.3 | 75 | 35*60 | 6.3 | 6.9 | |
2.7 | 500 | 3.4 | 2.9 | 1.3 | 80 | 35*67 | 6.3 | 6.7 | |
2.7 | 600 | 3.5 | 3 | 1.5 | 82 | 35*70 | 7.4 | 6.4 |
Product display:
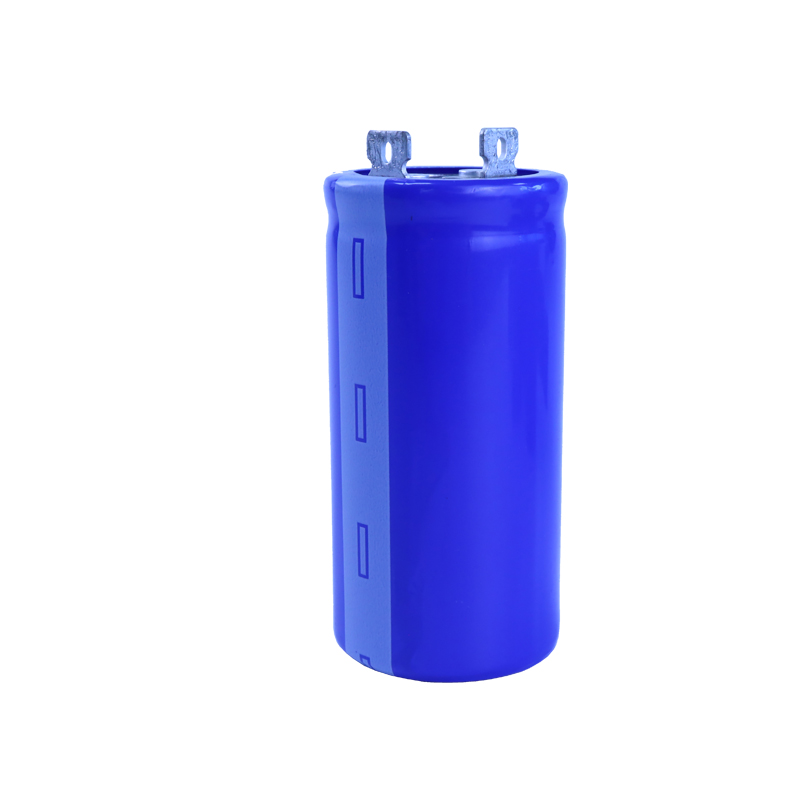
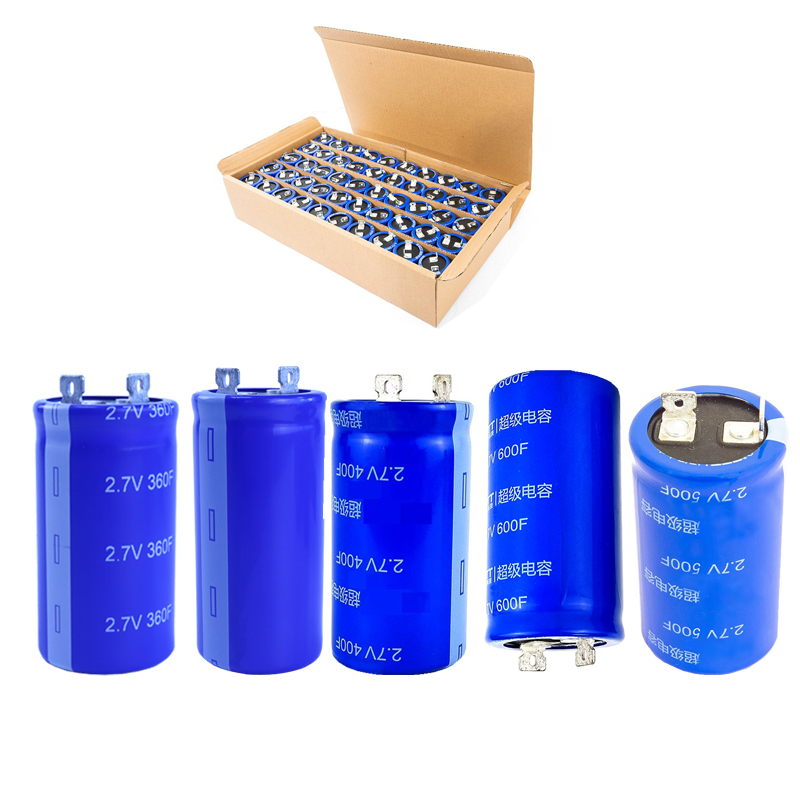


Product size:
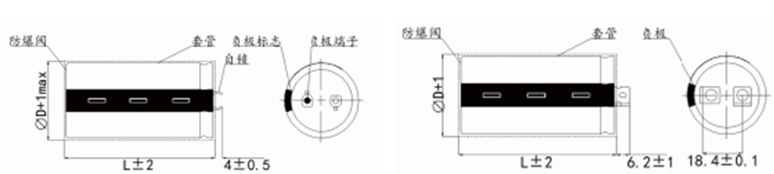
Application field:
1. Portable equipment: notebook computer, camera, PDA, digital camera, portable DVD, etc
2. Household appliances: two-way radio, interphone, electric toy, electric bicycle, emergency lighting
3. Military equipment
4. Medica
5. Electric tools
![1676271312160100.jpg 9KNWP1HKPP)MWOMO9}A%K]U.jpg](/data/upload/202302/1676271312160100.jpg)
The function of super farad capacitor:
1、 Its low internal resistance charging speed is very fast. 2、 If it can be recycled for a long time, it is equivalent to a large rechargeable battery. The number of times it can be recycled is about 500000, with high reliability. 3、 The discharge capacity of large current is strong, the energy conversion efficiency is very high, and there is almost no loss in the conversion process. 4、 The resistance to temperature is very strong. The super Farad capacitor can withstand both high and low temperatures. 5、 No special control of charging and discharging circuits is required. 6、 It is very convenient to detect the remaining power of the super farad capacitor, which can be seen directly. Finally, the super Farad capacitor is very environmentally friendly. Compared with other parts, the super Farad capacitor is also a kind of green energy.
Super Farad capacitors can be used for many applications. Here are two examples:
1. Flashlight
It is very frustrating to find that flashlights are getting dimmer and dimmer in emergency situations, because the battery life has expired. Even modern flashlights need several hours to be fully charged, and the cycle life of the battery is very short. All this may become history. A flashlight that uses supercapacitors instead of batteries as energy storage elements, only takes 90 seconds to charge, and its cycle life can reach 500000 times.
2. DC panel energy storage system
As a power supply, the DC panel plays a very important role in the power supply system of substations, power plants, large and medium-sized factories and mining enterprises. It is mainly used to supply power to the transmission mechanism of control, protection, communication equipment, automatic device operating machinery and regulating machinery. At the same time, it can also be used as an independent emergency lighting power supply, so its performance and reliability directly affect the normal and safe operation of the entire power supply system.
Test method:
1. Electrostatic capacity tester
(1) Test principle
The electrostatic capacity of supercapacitors is measured by the method of constant current discharge of capacitors, and calculated according to the formula. C=It (U1-U2), where: C-electrostatic capacity, F; I - constant discharge current, A; U1 and U2 adopt voltage, V; Discharge time required for t-U1 to U2, S
(2) Test procedure
Charge the capacitor with a current of 100A, charge the capacitor to the working voltage and keep the voltage constant for 10 seconds, then discharge the capacitor with a current of 100A, take U1 as 1.2VU2 as 1.0V, record the discharge time within the voltage range, the total cycle static capacity, take the average
2. Stored energy
(1) Test
The energy test of supercapacitors is carried out by discharging the capacitor at constant power to 1/2 working voltage within the given voltage range of the capacitor. The output energy W of capacitor is obtained from the relationship between constant discharge power P and discharge time T, that is, W=P. T
(2) Test procedure
Charge the capacitor to the working voltage with a constant current of 100A, and then, until the charging current drops to the specified current (traction type 10A, starting type 1A). After 5 seconds of standstill, discharge the capacitor to 1/2 of the working voltage with a constant power, record the discharge time and calculate the value. Cycle 3 measurements and take the average value
3. Equivalent series resistance test (DC)
(1) Test principle
The internal resistance of the capacitor is measured according to the sudden change of voltage within 10 milliseconds after the capacitor is disconnected from the constant current charging circuit. That is, in the formula: R-internal resistance of capacitor; U0 - voltage before the capacitor cuts off the charge; Ui - cut off the voltage within 10 ms after charging; I - Cut off the current before charging.
(2) Measurement process
Charge the capacitor with a constant current of 100A, disconnect the charging circuit at 80% of the charging working voltage, use the sampling machine to record the voltage change value within 10 ms after the capacitor is powered off, and calculate the internal resistance, repeat for 3 times, and take the average value.
4. Leakage current test
After the capacitor is charged to the rated voltage with a constant current of 100A, it is charged at this voltage for 30min at constant voltage, and then left open for 72h. In the first three hours, record the voltage value every minute, and in the remaining time, record the voltage value every ten minutes.
Calculate the self-discharge energy loss, SDLF=1 - (V/VW) 2, and the calculation time points are: 0.5,1,8,24,36,72 h
Note: The voltage tester must have a high input impedance to minimize the playback noise.
Usage:
Super capacitors cannot be used in the following states:
1) Temperature above nominal temperature
When the temperature of the capacitor exceeds the nominal temperature, the electrolyte will decompose, and the capacitor will heat up, the capacity will drop, and the internal resistance will increase, and the service life will be shortened.
2) Voltage exceeding rated voltage
When the voltage of the capacitor exceeds the nominal voltage, the electrolyte will decompose, and the capacitor will heat up, the capacity will drop, and the internal resistance will increase, and the service life will be shortened. Therefore, reducing the service voltage can improve the service life.
3) Reverse voltage or AC voltage loading
1. Influence of ambient temperature on supercapacitors The service life of supercapacitors is affected by the service temperature. Generally, if the service temperature is increased by 10 ℃, the service life of supercapacitors will be shortened by half. Please try to use in a low temperature environment below the service temperature. If it is used beyond the service temperature, it may cause sharp deterioration and damage of the characteristics. The operating temperature of the supercapacitor should not only confirm the ambient temperature and internal temperature of the equipment, but also confirm the radiation heat of the heating elements (power transistors, resistors, etc.) in the equipment and the self-heating temperature caused by the ripple current. In addition, do not install the heater near the supercapacitor.
2. Please use it correctly according to the positive and negative pole marks of the capacitor.
3. Please avoid using supercapacitors in the following environments.
a) The environment of direct splashing water, salt water and oil, or the environment of condensation and full of gaseous oil or salt. b) An environment full of harmful gases (hydrogen sulfide, sulfite, chlorine, ammonia, bromine, methyl bromide, etc.). c) The environment splashed with acid and alkaline solvents. d) Environment with direct sunlight or dust. e) An environment subject to excessive vibration and shock.
4. Avoid overheating the capacitor during welding (for 1.6mm printed circuit board, the temperature should be 260 ℃ during welding, and the time should not exceed 5s).
5. Please avoid conducting circuit wiring between the outgoing electrodes of the supercapacitor or between the solder joints of the connecting plate.
6. Overvoltage and exceeding the operating temperature range may cause the pressure valve to act and the electrolyte will spray out. Therefore, please use the design method that has considered the possibility of this abnormal condition.
7. During fast charging and discharging, the voltage drop (also called IR drop) caused by internal impedance will occur at the beginning of charging and discharging. Therefore, please use the design method that has taken into account the amplitude of voltage change.
8. If the terminals of power-type large-capacity products (about 10F or above) are short-circuited under the charging state, there will be hundreds of amperes of current flowing through them, which is dangerous. Please do not install and remove it under charging state.
9. Do not put the capacitor into the dissolved solder, only stick the solder on the guide pin of the capacitor. Do not allow the welding rod to contact the heat-shrinkable tube of the capacitor.
10. Do not twist or tilt the capacitor forcibly after installation.
11. When the supercapacitors are used in series, there is a problem of voltage balance between the monomers